Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, businesses need to share information securely and efficiently across teams, partners, and customers. Traditional methods—like FTP transfers or duplicating datasets—are slow, costly, and prone to compliance risks. Enter Snowflake Data Sharing, a game-changing feature that enables real-time, secure, and zero-copy data exchange.
At CloudEQS, we’ve seen firsthand how Snowflake’s architecture transforms data collaboration. In this blog, we’ll explore what Snowflake Data Sharing is, why it matters, and how companies like OpenTug leveraged it to scale their operations.
The Problem
Traditional data sharing methods create major challenges for modern businesses. Organizations often struggle with data silos, duplicated datasets, and slow batch transfers that delay insights. In Traditional Data Sharing, provider has to do following.
- Extract the data from Source System
- Encrypt the Data
- Share the data to respective data consumers using FTP/API/Cloud Storage
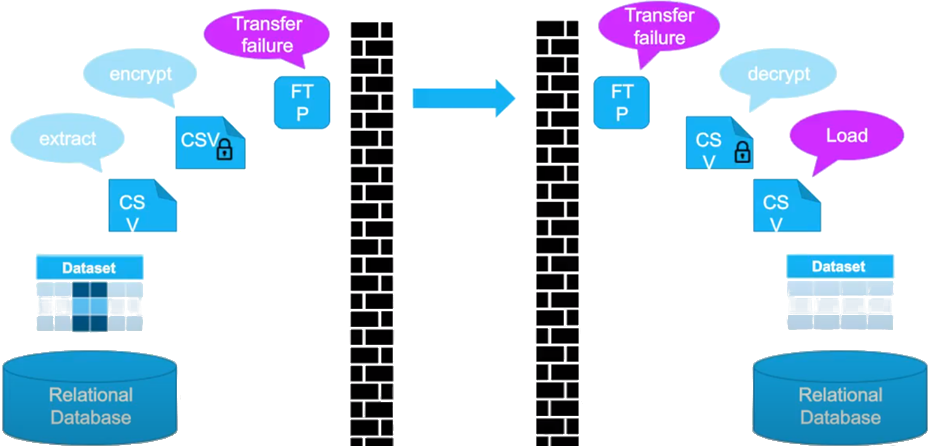
An outdated and highly error-prone process that results in:
- Increase storage costs
- Compliance risks
- Handling increased data size
- Decrypting sensitive data
- Changing file formats and schema
- Sharing data in real time Cleaning data
Making it virtually impossible to access data in real-time. Creating inefficiencies that hinder growth and innovation.
What is Snowflake Data Sharing?
Snowflake Data Sharing allows organizations to share live, governed data without moving or copying it. Unlike legacy approaches, Snowflake uses a single source of truth, ensuring:
- Zero-copy sharing: No duplication, reducing storage costs.
- Real-time access: Consumers always see the latest data.
- Secure governance: Role-based access and compliance controls.
What Are The Types of Snowflake Data Sharing?
Snowflake offers 3 types sharing options:
- Direct Share: Share data with other Snowflake accounts.
- Reader Accounts: Provide access to partners without Snowflake licenses.
- Snowflake Marketplace: Monetize data assets globally.
When providing data through a share, you can either share data with another Snowflake account or through reader accounts. When sharing data with another Snowflake account, the consumer is responsible for the compute objects (virtual warehouses) used to query the shared data.
Best Practices for Implementing Snowflake Data Sharing
- Define governance policies before sharing.
- Use secure roles and masking policies for sensitive data.
- Monitor usage and optimize performance regularly.
- Define who is going to pay for compute resources.
Conclusion
Snowflake Data Sharing isn’t just a feature—it’s a strategic enabler for modern businesses. Whether you’re looking to break down silos, collaborate with partners, or monetize your data, Snowflake provides the tools to do it securely and efficiently.
Ready to unlock the power of data sharing? Contact CloudEQS today to learn how we can help you design a smarter data architecture.


Comments are closed