Overview
As a follow‑up to the industry perspective outlined in Reducing Risk with Strong HIPAA‑Compliant Storage, this article zeroes in on what it actually takes to protect PHI in Azure.
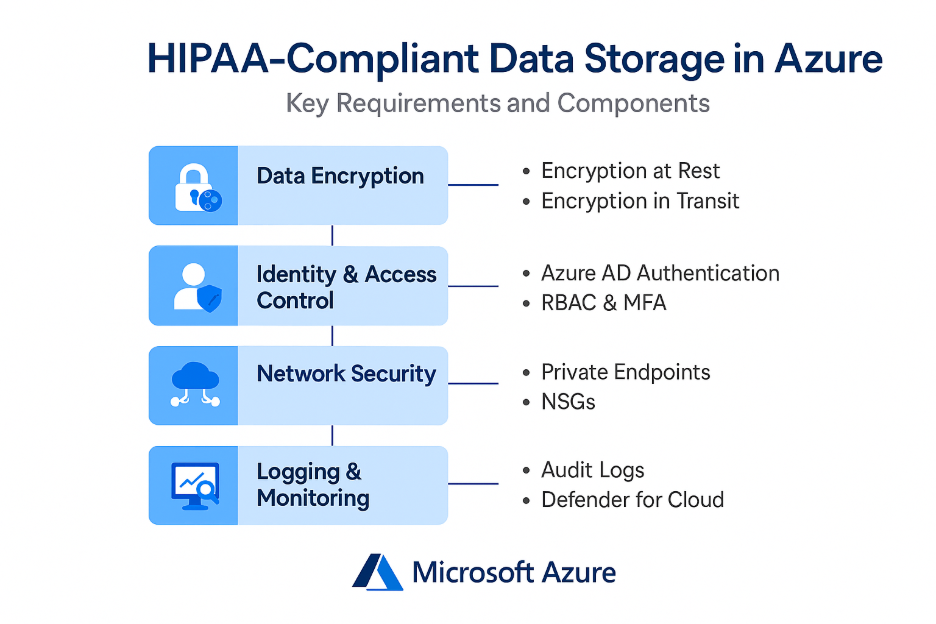
Below are the steps to follow to create a HIPPA compliant Azure Virtual Machines and Blog Storage.
1. Data Encryption: Protecting PHI at Rest and in Transit
- Encryption at Rest – The environment uses Storage Service Encryption (SSE) with Microsoft‑managed keys, ensuring PHI stored in Azure Blob Storage is protected at all times. Infrastructure‑level encryption was also enabled for added security.
- Encryption in Transit – All data access requires HTTPS endpoints, and TLS 1.2+ is enforced on VMs to protect data moving across networks.
2. Identity, Access Control & Least-Privilege Architecture
- Azure AD Authentication – To enforce secure authentication, Azure AD is enabled for Blob Storage access—reducing reliance on shared keys or account-level access.
- Managed Identities – System‑assigned managed identities were configured and granted the Storage Blob Data Contributor role, ensuring applications access storage securely without stored credentials.
- RBAC (Role‑Based Access Control) – All access follows the least‑privilege principle, controlling who can access what and limiting lateral movement.
- Multi‑Factor Authentication – While admin MFA is required, additional MFA for SSH access was also recommended to close remaining security gaps.
3. Network Security: Blocking Unwanted Traffic & Enabling Private Access
- Private Endpoints – Private Endpoints ensure Blob Storage is only accessible through the organization’s internal network—eliminating public exposure.
- Network Security Groups – NSGs are configured to block unnecessary inbound traffic, with HTTP disabled and HTTPS strictly enforced.
- Public Access Disabled – Anonymous Blob access is disabled across all storage layers.
4. Logging, Monitoring & Threat Protection
HIPAA requires full visibility into system activities. Thus the following is required:
- Azure Monitor configuration for security and performance logs
- Diagnostic Logs (in progress) to capture detailed storage‑level access events
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud for threat detection, Just‑in‑Time access, and vulnerability scanning (enhanced plan recommended)
This continuous monitoring ensures early detection of suspicious activity and supports mandatory audit trails.
5. Backup, Recovery & Data Retention Controls
- Soft Delete Enabled – Soft delete protects against accidental deletion:
- Blobs: 7 days
- Containers: 7 days
This aligns with healthcare data retention best practices and enables robust recovery procedures.
6. Compliance Governance & Microsoft BAA
To finalize HIPAA readiness, the environment required:
- Regular security assessments (free in Azure Defender)
- Signing Microsoft’s Business Associate Agreement (BAA)
Completion of the BAA ensures Microsoft is contractually responsible for safeguarding PHI under HIPAA.
Summary
By leveraging Azure’s comprehensive security and compliance ecosystem, CIOs can confidently advance digital transformation while ensuring PHI remains protected across every layer of the environment.
If your organization is ready to modernize its data infrastructure, strengthen compliance, or accelerate cloud adoption, CloudEQS can guide you every step of the way.


Comments are closed